"""
File Encryptor Tool v0.05
Description:
This application provides a graphical user interface (GUI) for users to
encrypt and decrypt files. It employs a symmetric encryption technique
using the Fernet encryption scheme, which is built on top of the
cryptography library. The tool ensures that data is encrypted in
a secure and authenticated manner.
The resulting jsons files can be transferred or stored safely.
Note that the "cleartext" option will save the base64 version in cleartext
Files saved are clearly marked "cleartext" or "encrypted".
Remnants of clear text files can be recovered from memory and disk!
Installation:
# For Windows:
1. Create the virtual environment
python -m venv file_encryptor
2. Navigate to the environment and activate it
cd file_encryptor
scripts\activate
3. Upgrade pip and install necessary modules
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
python -m pip install -r requirements.txt
4. Execute the script
python thescript.py
# For MAC/Linux:
1. Create the virtual environment
python3 -m venv file_encryptor
2. Navigate to the environment and activate it
cd file_encryptor
source bin/activate
3. Upgrade pip and install necessary modules
python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip
python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt
4. Execute the script
python3 thescript.py
# Note: You only need to create the environment and install modules once.
# Thereafter, just activate the environment and run the script.
Encryption Details:
- Encryption Type: Fernet (symmetric encryption)
- Underlying Algorithm: AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) in CBC mode with a 128-bit key
- Key Derivation: SHA-256 hash of the user's password, followed by URL-safe Base64 encoding
- Additional Data Protection: HMAC using SHA256 for integrity and authenticity
- File data is first encoded in Base64 format before encryption
Other Features:
- Option to save the file data in clear text Base64 format
- Encrypted data is stored in a JSON file, with filename and MD5 hash for verification
- GUI built with tkinter for facilitate file selection, encryption, and decryption
Modules Used:
- base64: For encoding and decoding file data
- hashlib: For generating MD5 hash and key derivation
- json: For storing encrypted data in JSON format
- os, datetime: Utility modules for file handling and timestamp generation
- tkinter: For the GUI components
- cryptography.fernet: For the Fernet encryption scheme
Usage:
Simply run the application, follow the GUI prompts to select a file, set a password,
and choose whether to encrypt or decrypt. The encrypted or decrypted result will be
saved as a new file in the current directory.
Note:
Always remember the password used for encryption, as there's no way to recover the original
file without it. Also, due to the symmetric nature of Fernet, the same key (derived from the
password) is used for both encryption and decryption.
Fun Facts:
Hash tables, are near instant lookups, but building them takes tremendous resources
power and storage. Building them with specific rules such as with formats like:
Word1, Word2, Special would greatly reduce the table size, but allow for
easy lookups of anything that matched that format.
High entropy (passwords like JKL(^&@HJA))2220akasuw28) are more effective against
these types of attacks, but in reality are a pain in the ass to remember.
You need to balance use of something easy (like: Dragon&Wendigo@81) vs something
with more entropy but impossible to remember (like: D*@JiUsywl_+2*&/sq)
For fun, here is what a full brute force attack would take, compared to rainbow tables,
or at least, estimates if they could guess at 2 Billion Guesses a second and
needed to guess all possible combinations.
Remember, 100000 GPU each doing 2 Billion Guesses in parallel could shave this time
down considerably.
Storing the guess as a hash requires space, so by making the storage and computational
power requirements excessive, the hope is to limit 3 letter agencies from accessing
encrypted data. In reality they want this for military use as well, so it's
well funded.
In reality, salted hashes make rainbow tables obsolete, but for fun:
| Length | Combos (95^n) | Brute Time | Size ( TB) | Hash Time |
|--------|---------------|--------------|------------|--------------|
| 10 | 2.59x10^19 | 1295 years | 8.27 PB | Near-instant |
| 12 | 5.62x10^23 | 8.89 m years | 1.80 EB | Near-instant |
| 14 | 1.22x10^28 | 1.93 b years | 3.89 ZB | Near-instant | <-- recommended size
| 16 | 2.64x10^32 | 4.19 t years | 844 YB | Near-instant |
Rainbow Table Storage Size:
Byte (B)
Kilobyte (KB) = 1,024 B
Megabyte (MB) = 1,024 KB
Gigabyte (GB) = 1,024 MB
Terabyte (TB) = 1,024 GB
Petabyte (PB) = 1,024 TB
Exabyte (EB) = 1,024 PB
Zettabyte (ZB) = 1,024 EB
Yottabyte (YB) = 1,024 ZB
Petabytes (PB):
Storing data in the Petabyte range is not uncommon for large enterprises or cloud
service providers. Large datasets, such as those used for machine learning, can get
into the PB range.
Physical Storage: A single Snowmobile can transport up to 100 PB of data.
(PB is easily doable for 3 letter agencies and likely they have multiple tables already)
Exabytes (EB):
No individual company or service is known to store data in the EB range
but globally, companies combined are generating and storing data in this range.
Physical Storage: AWS Snowmobile can be used multiple times for such transfers.
Zettabytes (ZB):
The total data stored globally, combining all companies, services, and personal data,
has been projected to reach the ZB range. However, no single entity has ZB-scale storage.
Services: Currently, no specific service offers ZB capacity, but the combined capacity
of all global data centers might be approaching this figure.
Yottabytes (YB):
This is mostly theoretical in current real-world scenarios. It's hard to fathom
storing YB-scale data with present technology.
Todo:
So, it would take Brute time to setup the table, but once done it can be cracked instantly
Storage and computational costs make this unlikely except for govt actors to consider.
todo: the use of a unique salt per password in conjunction with slow hashing functions
(like bcrypt, PBKDF2, or Argon2) can make pre-computed tables like rainbow tables
ineffective and significantly slow down brute-force attempts.
(there is no salt in this encryption protection, adding salt would be advised refactor)
Author:
James Fraze ([email protected])
"""
import base64
import hashlib
import json
import os
import re
from datetime import datetime
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk, filedialog, messagebox
from cryptography.fernet import Fernet, InvalidToken
def is_valid_password(password):
"""
Check if the given password meets the following criteria:
- At least one uppercase letter
- At least one lowercase letter
- At least one digit
- At least one symbol
- Minimum length of 14 characters
Args:
password (str): Password string to check
Returns:
bool: True if the password is valid, False otherwise
"""
# At least one upper case
if not re.search(r"[A-Z]", password):
return False
# At least one lower case
if not re.search(r"[a-z]", password):
return False
# At least one digit
if not re.search(r"[0-9]", password):
return False
# At least one symbol (non-alphanumeric character)
if not re.search(r"[^a-zA-Z0-9]", password):
return False
# At least 10 characters long
if len(password) < 14:
return False
return True
class App:
"""
Main application class for the File Encryptor tool.
"""
def __init__(self, root):
"""
Initialize the App with its GUI components.
Args:
root (tk.Tk): The main Tkinter window object
"""
# Setting the theme and global font size
style = ttk.Style()
style.theme_use("clam")
style.configure("TLabel", background="#d9d9d9")
style.configure(".", font=("Arial", 12))
self.root = root
self.file_path = None
# Adding an attribute to store the path to the loaded encrypted JSON
self.encrypted_json_path = None
# styles
style.configure(
"ReadOnly.TLabel",
background="#f0f0f0",
foreground="#808080",
relief=tk.GROOVE,
)
style.configure("ReadOnly.TEntry", background="#f0f0f0", foreground="#808080")
# checkbox variable
self.save_cleartext_var = tk.BooleanVar(value=False)
# Create a main frame with padding inside root
self.main_frame = ttk.Frame(root, padding=20)
self.main_frame.pack(padx=10, pady=10, expand=True, fill=tk.BOTH)
# Password
ttk.Label(self.main_frame, text="Password:").grid(
row=0, column=0, sticky="e", padx=10, pady=5
)
self.password_entry = ttk.Entry(
self.main_frame, show="*", width=20, font=("Arial", 12)
)
self.password_entry.grid(row=0, column=1, padx=10, pady=5, sticky="new")
self.cleartext_checkbox = ttk.Checkbutton(
self.main_frame, text="Cleartext", variable=self.save_cleartext_var
)
self.cleartext_checkbox.grid(row=0, column=3, padx=10, pady=5)
# Original File
ttk.Label(self.main_frame, text="Original File:").grid(
row=1, column=0, sticky="e", padx=10, pady=5
)
self.file_label = ttk.Label(
self.main_frame,
text="Choose File to Encrypt",
style="ReadOnly.TLabel",
width=50,
)
self.file_label.grid(row=1, column=1, padx=10, pady=5)
self.browse_button = ttk.Button(
self.main_frame, text="Browse", command=self.load_file
)
self.browse_button.grid(row=1, column=2, padx=10, pady=5)
self.encrypt_button = ttk.Button(
self.main_frame, text="Encrypt", command=self.encrypt
)
self.encrypt_button.grid(row=1, column=3, padx=10, pady=5)
# Original MD5
ttk.Label(self.main_frame, text="Original MD5:").grid(
row=2, column=0, sticky="e", padx=10, pady=5
)
self.md5_original_entry = ttk.Entry(
self.main_frame, state="readonly", style="ReadOnly.TEntry"
)
self.md5_original_entry.grid(row=2, column=1, padx=10, pady=5, sticky="we")
# Encrypted File
ttk.Label(self.main_frame, text="Encrypted File:").grid(
row=3, column=0, sticky="e", padx=10, pady=5
)
self.encrypted_file_label = ttk.Label(
self.main_frame,
text="Choose File to Decrypt",
style="ReadOnly.TLabel",
width=50,
)
self.encrypted_file_label.grid(row=3, column=1, padx=10, pady=5)
self.load_json_decrypted_button = ttk.Button(
self.main_frame, text="Browse", command=lambda: self.load_json("encrypted")
)
self.load_json_decrypted_button.grid(row=3, column=2, padx=10, pady=5)
self.decrypt_button = ttk.Button(
self.main_frame, text="Decrypt", command=self.decrypt
)
self.decrypt_button.grid(row=3, column=3, padx=10, pady=5)
# Encrypted MD5
ttk.Label(self.main_frame, text="Encrypted MD5:").grid(
row=4, column=0, sticky="e", padx=10, pady=5
)
self.md5_decrypted_entry = ttk.Entry(
self.main_frame, state="readonly", style="ReadOnly.TEntry"
)
self.md5_decrypted_entry.grid(row=4, column=1, padx=10, pady=5, sticky="we")
def load_file(self):
"""
Open a file dialog to let the user select a file.
Update the filename and its MD5 hash in the GUI.
"""
self.file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(filetypes=[("All Files", "*.*")])
if not self.file_path:
return
self.file_label.config(text=self.file_path)
# open file as binary
with open(self.file_path, "rb") as f:
content = f.read()
md5_value = hashlib.md5(content).hexdigest()
self.md5_original_entry.config(state="normal")
self.md5_original_entry.delete(0, tk.END)
self.md5_original_entry.insert(0, md5_value)
self.md5_original_entry.config(state="readonly")
def load_json(self, target):
"""
Open a file dialog to load a JSON file and update the GUI accordingly.
Args:
target (str): Either "original" or "encrypted" for file details.
"""
file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(
filetypes=[("JSON Files", "*.json"), ("All Files", "*.*")]
)
if not file_path:
return
with open(file_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as file:
data = json.load(file)
if target == "original":
# Load filename
self.file_label.config(text=data["filename"])
# Load MD5 hash
self.md5_original_entry.config(state="normal")
self.md5_original_entry.delete(0, tk.END)
self.md5_original_entry.insert(0, data["md5"])
self.md5_original_entry.config(state="readonly")
elif target == "encrypted":
# Check if it potentially is an encrypted file
if not (
"filename" in data and "md5" in data and "base64_encrypted" in data
):
messagebox.showerror(
"Error", "File structure is not valid for an encrypted file!"
)
return
if (
len(data["filename"]) < 40 or len(data["md5"]) < 40
): # Assuming at least 40 chars for encrypted values
messagebox.showerror(
"Error", "File content doesn't seem to be encrypted!"
)
return
# Store the path to the encrypted JSON file for decryption later
self.encrypted_file_label.config(text=file_path)
self.encrypted_json_path = file_path
def get_key(self):
"""
Generate an encryption key based on the password entered by the user.
Returns:
bytes: The generated encryption key
"""
key = hashlib.sha256(self.password_entry.get().encode()).digest()
return base64.urlsafe_b64encode(key)
def encrypt(self):
"""
Encrypt the selected file and generate a JSON with the encrypted data.
"""
phrase = self.password_entry.get()
if not is_valid_password(phrase):
messagebox.showerror(
"Error",
"Password Fail: Use 10 characters, digits, upper case, lower case, and symbols.",
)
return
if not self.file_path:
messagebox.showerror("Error", "Please select a file to encrypt!")
return
with open(self.file_path, "rb") as f:
content = f.read()
base64_encoded = base64.b64encode(content)
cipher = Fernet(self.get_key())
encrypted_data = cipher.encrypt(base64_encoded)
encrypted_filename = cipher.encrypt(self.file_path.encode()).decode()
encrypted_md5 = cipher.encrypt(self.md5_original_entry.get().encode()).decode()
# Save to JSON files when "Encrypt" button is pressed
md5_value = self.md5_original_entry.get()
if self.save_cleartext_var.get():
original_data = {
"filename": self.file_path,
"md5": md5_value,
"base64": base64_encoded.decode(
"utf-8"
), # Use the base64_encoded variable directly here.
}
self.save_to_json(f"cleartext_{md5_value}.json", original_data)
messagebox.showinfo(
"Info", "File has been saved in clear text base64 format"
)
# Use current date and time to format the filename
current_time = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
encrypted_data_json = {
"filename": encrypted_filename,
"md5": encrypted_md5,
"base64_encrypted": encrypted_data.decode("utf-8"),
}
self.save_to_json(f"encrypted_{current_time}.json", encrypted_data_json)
messagebox.showinfo("Info", "File has been saved in encrypted format")
def save_to_json(self, filename, data):
"""
Save the given data as a JSON file.
Args:
filename (str): The name of the file to save the data to.
data (dict): The data to save to the file.
"""
with open(filename, "w", encoding="utf-8") as file:
json.dump(data, file)
def decrypt(self):
"""
Decrypt a previously encrypted file and update the GUI with the decrypted details.
"""
phrase = self.password_entry.get()
if not phrase:
messagebox.showerror("Error", "Please enter an encryption phrase!")
return
if not self.encrypted_json_path:
messagebox.showerror("Error", "Please load an encrypted JSON file!")
return
# Load the JSON data from the stored path
with open(self.encrypted_json_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as file:
encrypted_data = json.load(file)
cipher = Fernet(self.get_key())
# Decrypt filename, md5, and base64 encrypted data
try:
decrypted_filename = cipher.decrypt(
encrypted_data["filename"].encode()
).decode()
decrypted_md5 = cipher.decrypt(encrypted_data["md5"].encode()).decode()
decrypted_base64_data = cipher.decrypt(
encrypted_data["base64_encrypted"].encode()
)
except InvalidToken:
messagebox.showerror("Error", "Decryption failed due to invalid token!")
return
except Exception as e:
messagebox.showerror("Error", f"Decryption failed! Error: {e}")
return
# Decode the decrypted base64 data to get the original file data
base64_decoded = base64.b64decode(decrypted_base64_data)
# Check decrypted filename length
if len(decrypted_filename) < 5:
messagebox.showerror("Error", "Invalid decrypted filename!")
return
# Write the decoded data to a file in the current script location
filename_only = os.path.basename(decrypted_filename)
with open(filename_only, "wb") as f:
f.write(base64_decoded)
# Calculate MD5 checksum of the decrypted file
md5_checksum = self.calculate_md5(filename_only)
# Update the UI with the decrypted data
self.file_label.config(text=decrypted_filename)
self.md5_original_entry.config(state="normal")
self.md5_original_entry.delete(0, tk.END)
self.md5_original_entry.insert(0, md5_checksum)
self.md5_original_entry.config(state="readonly")
self.md5_decrypted_entry.config(state="normal")
self.md5_decrypted_entry.delete(0, tk.END)
self.md5_decrypted_entry.insert(0, decrypted_md5)
self.md5_original_entry.config(state="readonly")
# Check MD5 checksum against decrypted value
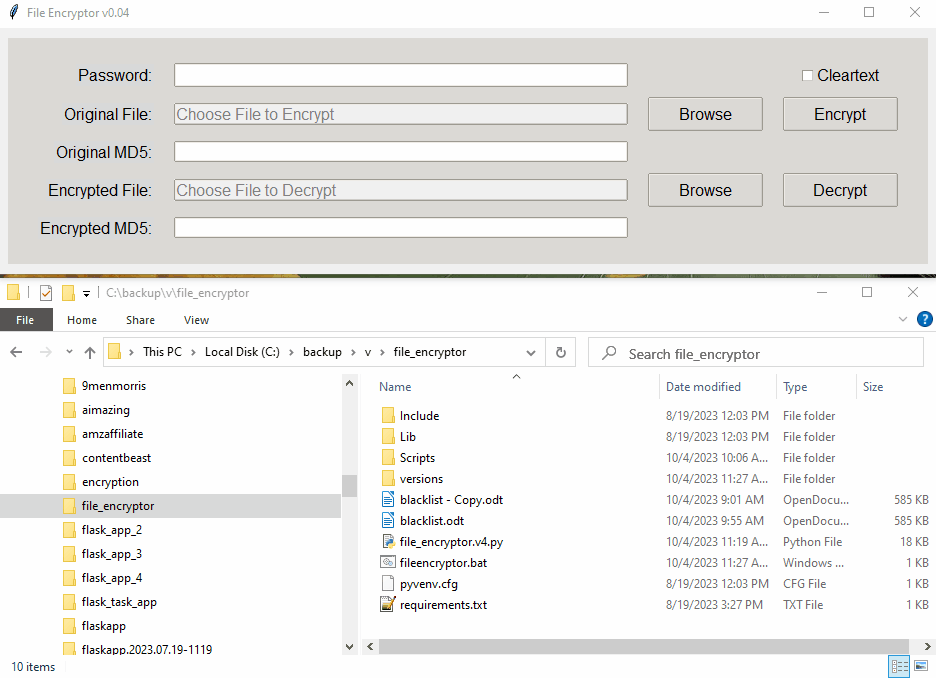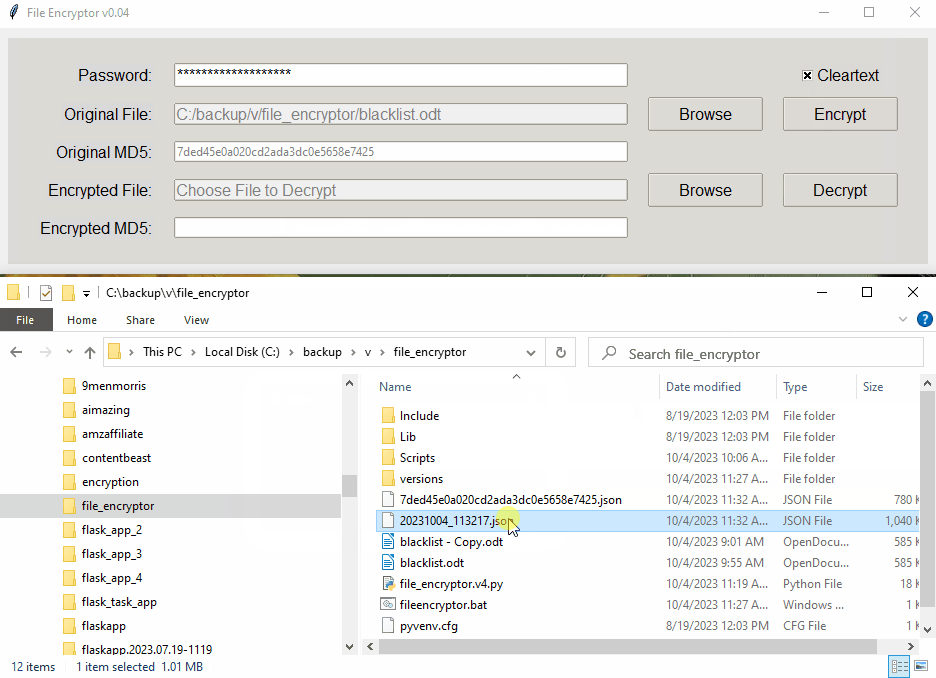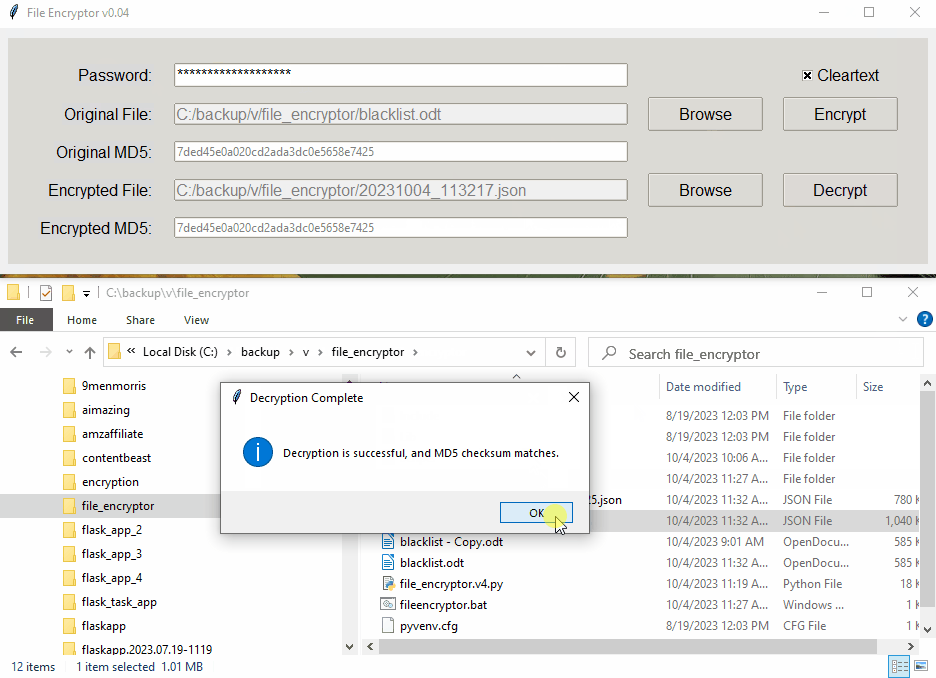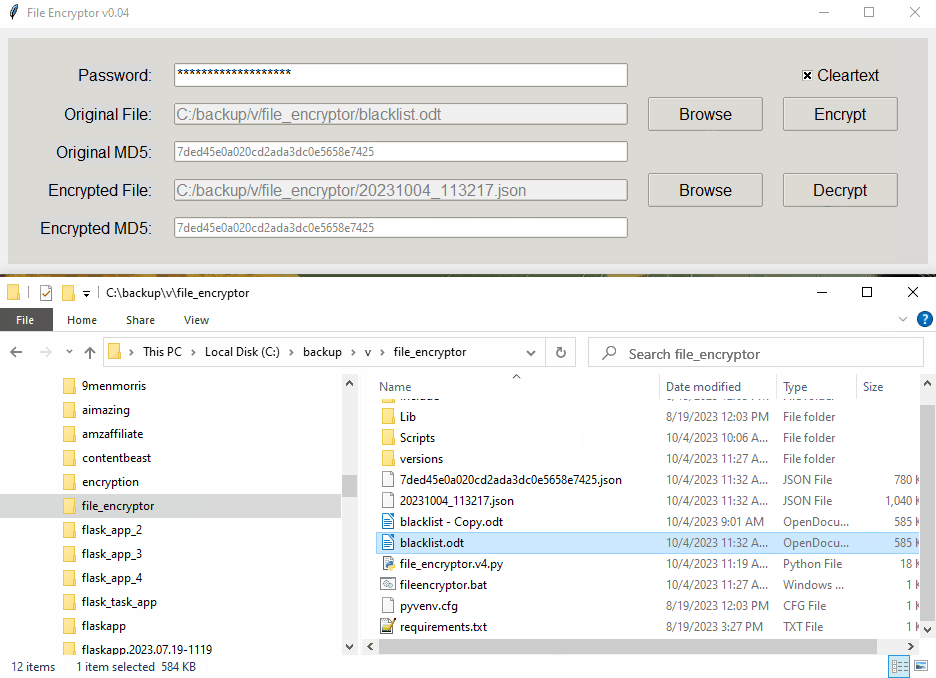
if decrypted_md5 == md5_checksum:
print(f"DECRYPTED MD5: {decrypted_md5}")
print(f"ORIGINAL MD5: {md5_checksum}")
messagebox.showinfo(
"Decryption Complete",
"Decryption is successful, and MD5 checksum matches.",
)
else:
print(f"DECRYPTED MD5: {decrypted_md5}")
print(f"ORIGINAL MD5: {md5_checksum}")
messagebox.showerror(
"Error", "Decryption completed, but MD5 checksum doesn't match!"
)
def calculate_md5(self, filename):
"""
Calculate the MD5 hash of a given file.
Args:
filename (str): Path to the file
Returns:
str: MD5 hash of the file
"""
hasher = hashlib.md5()
with open(filename, "rb") as f:
buf = f.read()
hasher.update(buf)
return hasher.hexdigest()
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("File Encryptor v0.05")
App(root)
root.mainloop()